AgML - Machine Learning for Agricultural Modeling
AgML is the AgMIP transdisciplinary community of agricultural and machine learning modelers.
AgML aspires to
identify key research gaps and opportunities at the intersection of agricultural modelling and machine learning research,
support enhanced collaboration and engagement between experts in these disciplines, and
conduct and publish protocol-based studies to establish best practices for robust machine learning use in agricultural modelling.
AgML Crop Yield Forecasting
The objective of AgML Crop Yield Forecasting task is to create a benchmark to compare models for crop yield forecasting across countries and crops. The models and forecasts can be used for food security planning or famine early warning. The benchmark is called CY-Bench (crop yield benchmark).
Table of contents
Overview
Early in-season predictions of crop yields can inform decisions at multiple levels of the food value chain from late-season agricultural management such as fertilization, harvest, and storage to import or export of produce. Anticipating crop yields is also important to ensure market transparency at the global level (e.g. Agriculture Market Information System, GEOGLAM Crop Monitor) and to plan response actions in food insecure countries at risk of food production shortfalls.
We propose CY-Bench, a dataset and benchmark for subnational crop yield forecasting, with coverage of major crop growing countries of the world for maize and wheat. By subnational, we mean the administrative level where yield statistics are published. When statistics are available for multiple levels, we pick the highest resolution. By yield, we mean end-of-season yield statistics as published by national statistics offices or similar entities representing a group of countries. By forecasting, we mean prediction is made ahead of harvest. The task is also called in-season crop yield forecasting. In-season forecasting is done at a number of time points during the growing season from mid-season to before harvest. The first forecast is made in the middle of the season, i.e. (end of season - start of the season)/2, between mid-season and harvest and 2 weeks before harvest. These time points depend on the crop calendar for the selected crop and country (or region). Since yield statistics may not be available for the current season, we evaluate models using predictors and yield statistics for all available years. The models and forecasts can be used for food security planning or famine early warning. We compare models, algorithms and architectures by keeping other parts of the workflow as similar as possible. For example: the dataset includes same source for each type of predictor (e.g. weather variables, soil moisture, evapotranspiration, remote sensing biomass indicators, soil properties), and selected data are preprocessed using the same pipeline (use the crop mask, crop calendar; use the same boundary files and approach for spatial aggregation) and (for algorithms that require feature design) and same feature design protocol.
Coverage for maize
Undifferentiated Maize or Grain Maize where differentiated 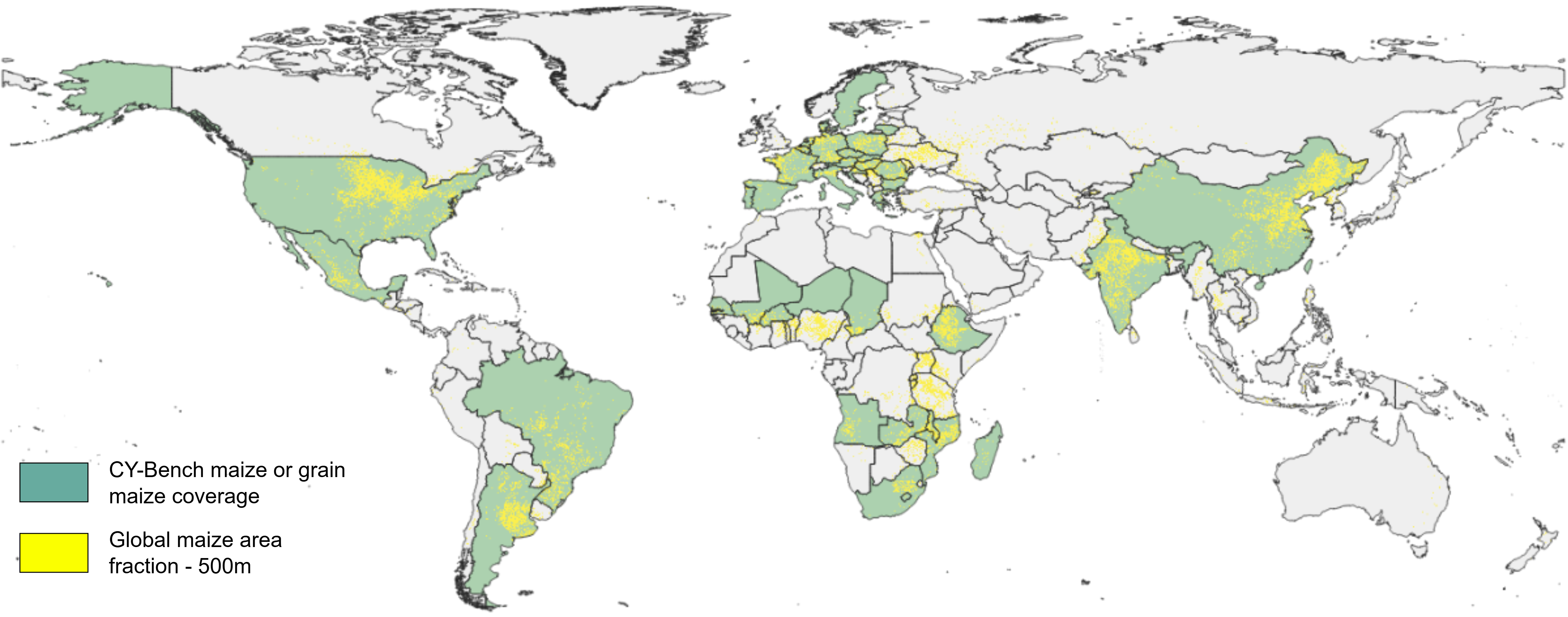
Coverage for wheat
Undifferentiated Wheat or Winter Wheat where differentiated 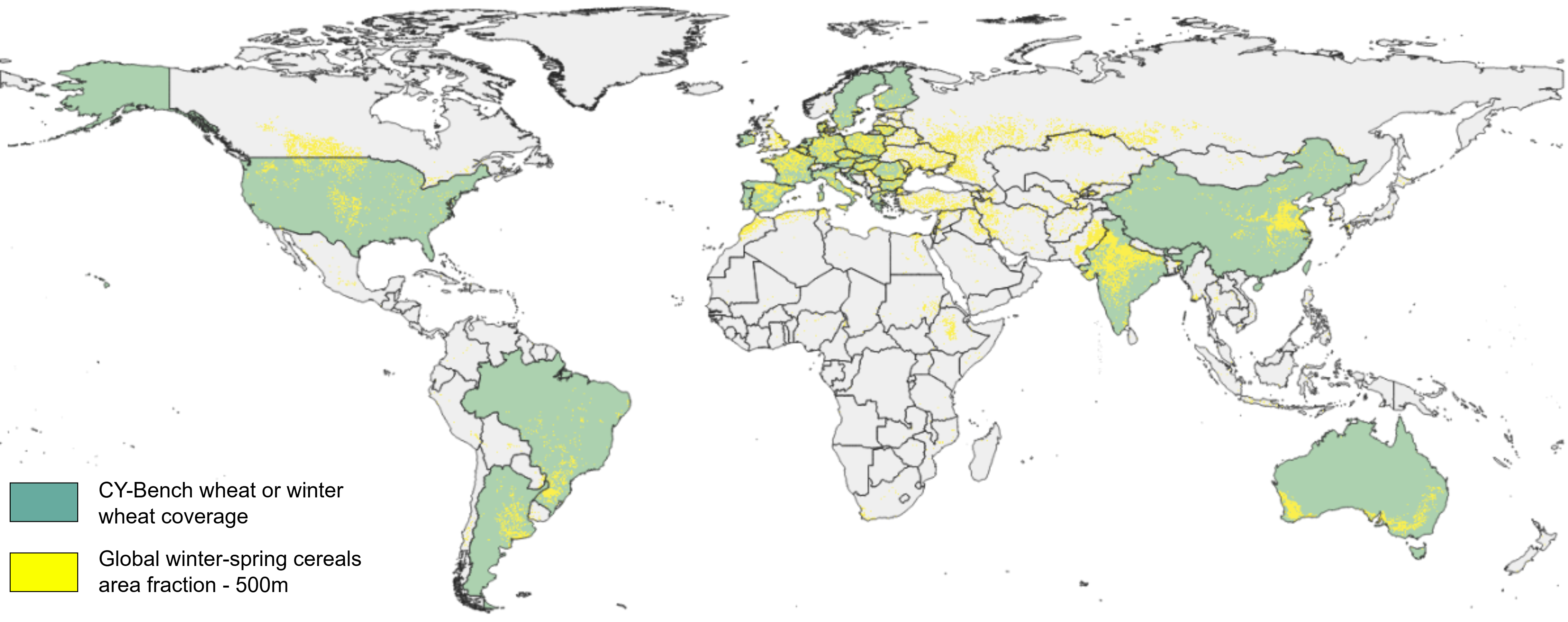
Getting started
cybench is an open source python library to load CY-Bench dataset and run the CY-Bench tasks.
Installation
git clone https://github.com/BigDataWUR/AgML-crop-yield-forecasting
Requirements
The benchmark results were produced in the following test environment:
Operating system:
CPU:
memory (RAM):
disk storage:
GPU:
Software requirements: Python 3.10, scikit-learn 1.3.2, PyTorch 2.1.1+cpu.
Downloading dataset
Get the dataset from Zenodo.
pip install zenodo_get
zenodo_get -r <record_number>
Running the benchmark
First write a model class your_model that extends the BaseModel class. The base model class definition is inside models.model.
from cybench.models.model import BaseModel
from cybench.benchmark import run_cybench
class MyModel(BaseModel):
pass
my_model = MyModel()
dataset_name = "maize_us"
run_cybench(my_model, dataset_name)
Dataset
Dataset can be loaded by crop and (optionally by country).
For example
dataset = Dataset.load("maize")
will load data for countries covered by the maize dataset. Maize data for the US can be loaded as follows:
dataset = Dataset.load("maize_us")
Data sources
Crop Statistics |
Shapefiles or administrative boundaries |
Predictors, crop masks, crop calendars |
|---|---|---|
Weather: AgERA5 |
||
Mali1 |
Use Africa shapefiles from FEWSNET |
Soil: WISE soil data |
Soil moisture: GLDAS |
||
Evapotranspiration: FAO |
||
FAPAR: JRC FAPAR |
||
Crop calendars: ESA WorldCereal |
||
NDVI: MOD09CMG |
||
Use EU shapefiles |
Crop Masks: ESA WorldCereal |
|
1: Mali data at admin level 3. Mali data is also included in the FEWSNET Africa dataset, but there it is at admin level 1. 2: Germany data at admin level 3. Germany data is also included in the EU dataset, but there it is at admin level 1.
Leaderboard
Model Name |
NRMSE |
MAPE |
|---|---|---|
AverageYieldModel |
||
Linear TrendModel |
||
Ridge (sklearn) |
||
TorchLSTMModel |
How to cite
Please cite CY-bench as follows: TODO.
How to contribute
Thank you for your interest in contributing to AgML Crop Yield Forecasting. Please check contributing guidelines for how to get involved and contribute.
Additional information
For more information please visit the AgML website.